Mini/Midi - HDD
Design Guidelines - Mini-HDD
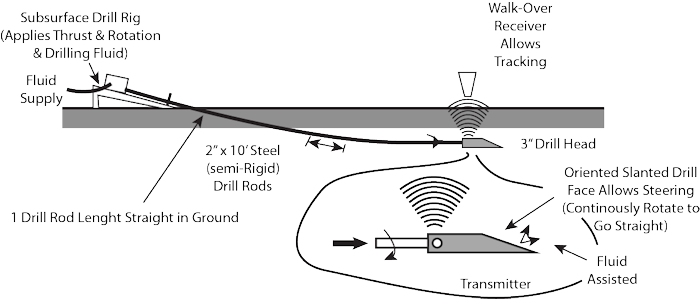
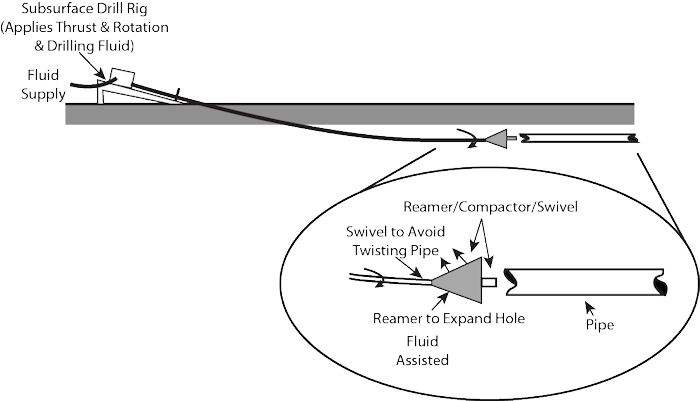
Pilot Boring and Pull-Back Operation
(Source: Outside Plant Consulting Services, Inc.)
While considered convenient and practical to apply by experienced engineers for a maxi-HDD operation, the overall ASTM International F1962 procedure and guidelines represent a relatively extensive, tedious process, when considering smaller, lower cost operations associated with typical mini-HDD applications. Mini-HDD operations are often performed during an upgrade of a large community, comprising many individual installations, with any single installation typically not receiving extensive investigation or analysis. Nonetheless, some mini-HDD installations may be considered to be relatively critical, or approach limits with respect to the capability of the available drill rig and/or the strength of the product pipe being installed. Furthermore, any construction procedure must address basic safety rules, avoid damage to existing facilities, adhere to applicable government regulations, and consider environmental issues. TR-46, Guidelines for Use of Mini-Horizontal Directional Drilling for Placement of High Density Polyethylene Pipe, was therefore developed to serve as an inclusive document, providing practices for selection and placement of HDPE pipe using mini-HDD.
Design Guidelines - Midi-HDD
Midi-HDD may be employed for boring paths up to 1,000 feet in length, at depths as much as 75 feet, and placing pipes up to 24 inches diameter. Midi-HDD equipment may be used for crossing beneath rivers and roadways. Although the TR-46 guidelines are primarily intended for mini-HDD operations, depending on the particular project, the information may also be applicable to a midi-HDD installation. Thus, guidelines for the use of midi-HDD machines and associated practices, including pipe selection methodology, may be obtained from the TR-46 document and/or ASTM F 1962, depending upon the judgment of the contractor or engineer.